IEC 60068-2-14 Test N: Change of Temperature - Ensuring Component Performance in Rapid Change Environments
Standard: IEC 60068-2-14 – Environmental Testing – Part 2-14: Tests – Test N: Change of Temperature
Scope: IEC 60068-2-14: Test N: Change of Temperature evaluates a product’s ability to withstand rapid or successive changes in temperature. It simulates environmental conditions where components may experience thermal stress due to sudden temperature transitions, such as moving from indoor to outdoor environments or exposure to cold water or rain. It is essential for assessing both mechanical integrity and functional performance under thermal cycling.
Applicable Products:
This standard applies to a wide range of components and systems, including:
- Electronic control units (ECUs)
- Sensors and actuators
- Battery systems
- Lighting and display systems
- Enclosures and mechanical assemblies
- Any product exposed to fluctuating thermal environments
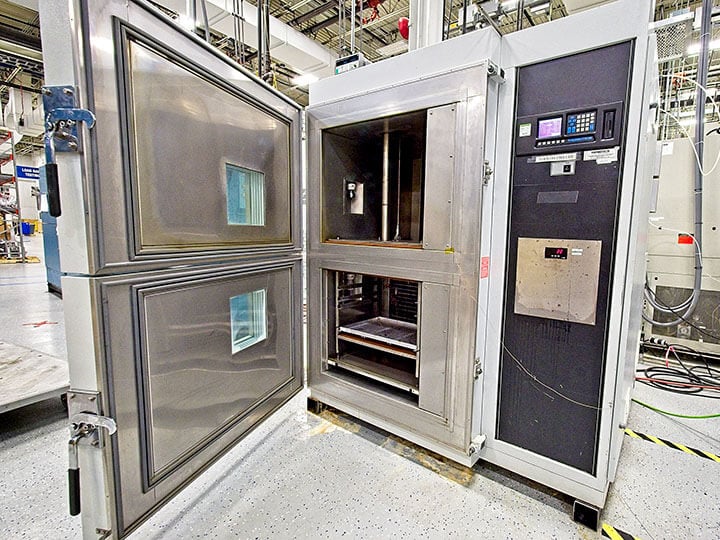
Test Procedure: In our specialized test lab, we conduct IEC 60068-2-14 Test N: Change of Temperature using state‑of‑the‑art equipment to ensure accurate and reliable results. The test procedures include:
- Test Na – Rapid Change of Temperature (Air-to-Air): The specimen is transferred between two chambers or zones with fixed high and low temperatures. Transfer time is minimized (typically <1 minute) to create a thermal shock. Dwell times at each temperature are defined or developed to ensure thermal stabilization of air or part temperature. Commonly used for components that may experience sudden environmental changes.
- Test Nb – Gradual Change of Temperature (Controlled Rate): The specimen remains in a single chamber where temperature changes at a controlled rate (typically 1 K/min to 15 K/min). This method simulates more gradual environmental transitions. Ideal for evaluating stress from internal heating or slow ambient changes. Often used for larger or more sensitive components.
- Test Nc – Rapid Change with Liquid-to-Liquid or Air-to-Liquid Transfer: The specimen is rapidly transferred between two liquid baths or from air to liquid. This method creates extreme thermal shock and is used for highly robust components. Less common but critical for specific high-stress applications. This test ensures components can endure thermal shock and maintain functionality under real-world temperature variations.
End Result: Successful completion of IEC 60068-2-14 Test N: Change of Temperature confirms that the product can tolerate rapid temperature changes without compromising structural integrity or performance.
Lab Locations: Detroit (Plymouth), MI; Grand Rapids (Kentwood), MI
You may be interested in...
Thermal Shock Testing Services
Thermal Shock testing is a critical tool for ensuring safety, performance, and customer satisfaction in temperature-sensitive applications.
Accelerated Stress Testing (AST)
Intertek offers Accelerated Stress Testing (AST) simulating “real-life” conditions to provide evaluation data that helps ensure a product’s life and reliability.
Products Failure Analysis and Materials Testing
Our Products Failure Analysis services improve product quality and apply to a variety of manufactured products, components and materials, including metals, plastics, electronics, and more.
Knowledge Center
Buzz, Squeak, and Rattle (BSR) Testing in Automotive Development Webinar
Master FMVSS 108 Compliance – Download the Expert Guide
Automotive Functional Safety & Cyber Security FAQs
Development of Driveline Electrification Technologies White Paper
Understanding Failure Analysis and Answering your Frequently Asked Questions
The Top-7 FAQs of Autonomous Vehicles Testing
The Top-10 FAQs of Advanced Composites Testing
The Top-10 FAQs of Automotive Interior Testing
Accelerated Stress Testing to Manage Disruptive Market Changes Webinar
Transitioning to Structural Composites to Meet CAFE Standards
Automotive Interiors Testing White Paper
Resources
Global Research & Certification
SatelliteTM Client Test Program
Engineering and Technical Staffing
SupplyTek - gain the confidence to go to market faster
Protek - safeguard people, systems and processes, facilities, materials and surfaces, and products